what is a dka coma Dka ketoacidosis diabetic diabetes medbullets step management insulin type endocrine pco2 mellitus nursing step1 po2
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious condition that can occur in individuals with diabetes, particularly those with type 1 diabetes. It is characterized by high blood sugar levels, a shortage of insulin, and the presence of ketones in the urine. DKA can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. In this post, we will explore the clinical aspects of DKA and discuss a mnemonic approach to understanding this condition.
Understanding DKA:
 When a person has insufficient insulin levels, the body is unable to properly use glucose as a source of energy. As a result, the body starts breaking down fat for energy, leading to the formation of ketones. These ketones accumulate in the blood and can cause a state of ketoacidosis.
When a person has insufficient insulin levels, the body is unable to properly use glucose as a source of energy. As a result, the body starts breaking down fat for energy, leading to the formation of ketones. These ketones accumulate in the blood and can cause a state of ketoacidosis.
The signs and symptoms of DKA can develop rapidly and may include frequent urination, excessive thirst, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, confusion, fruity-scented breath, and rapid breathing. If left untreated, DKA can lead to dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and even coma.
A Mnemonic Approach:
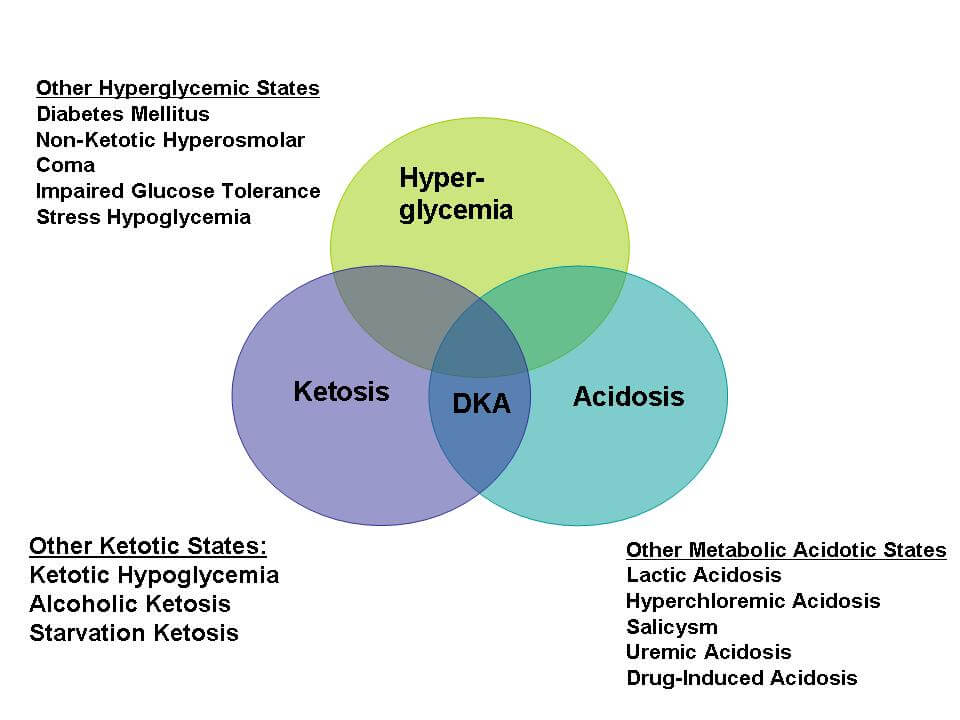 Remembering the key aspects of DKA can be made easier by using a simple mnemonic:
Remembering the key aspects of DKA can be made easier by using a simple mnemonic:
D: Dehydration
Dehydration is a common feature of DKA and occurs due to excessive urination caused by high blood sugar levels. The body tries to eliminate the excess sugar through urine, leading to fluid loss.
K: Ketosis
Ketosis refers to the production and accumulation of ketones in the blood. Ketones are formed as a result of the breakdown of fatty acids for energy when glucose is not readily available.
A: Acidosis
Acidosis occurs when the blood becomes too acidic due to the accumulation of ketones. This can lead to symptoms such as deep and rapid breathing, as the body attempts to exhale excess acid.
By remembering the DKA mnemonic, individuals can quickly recall the core features of this condition, aiding in its recognition and prompt management.
In conclusion, Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that requires immediate medical attention. By understanding the clinical aspects of DKA and utilizing the mnemonic approach, individuals will be better equipped to recognize the symptoms and seek appropriate treatment. If you or someone you know experiences symptoms of DKA, it is essential to seek medical assistance promptly to prevent potentially life-threatening complications.
If you are looking for Pin on Diabetes you’ve visit to the right page. We have 5 Pictures about Pin on Diabetes like Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hypersmolar Non-ketotic coma - The Clinical, Pin on Diabetes and also Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hypersmolar Non-ketotic coma - The Clinical. Here you go:
Pin On Diabetes
 www.pinterest.comcoma diabetic prevent hypoglycemia shaky causes glucose hyperglycemia diabetestalk
www.pinterest.comcoma diabetic prevent hypoglycemia shaky causes glucose hyperglycemia diabetestalk
DKA : Mnemonic Approach And Clinical Aspects | Epomedicine
 epomedicine.comdka hyperglycemic triad ketoacidosis diabetic hyperosmolar hyperglycemia mnemonic hhs state coma nonketotic crises clinical approach diabetes acidosis epomedicine ketotic causes
epomedicine.comdka hyperglycemic triad ketoacidosis diabetic hyperosmolar hyperglycemia mnemonic hhs state coma nonketotic crises clinical approach diabetes acidosis epomedicine ketotic causes
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) - Endocrine - Medbullets Step 1
 step1.medbullets.comdka ketoacidosis diabetic diabetes medbullets step management insulin type endocrine pco2 mellitus nursing step1 po2
step1.medbullets.comdka ketoacidosis diabetic diabetes medbullets step management insulin type endocrine pco2 mellitus nursing step1 po2
Diabetic Ketoacidosis And Hypersmolar Non-ketotic Coma - The Clinical
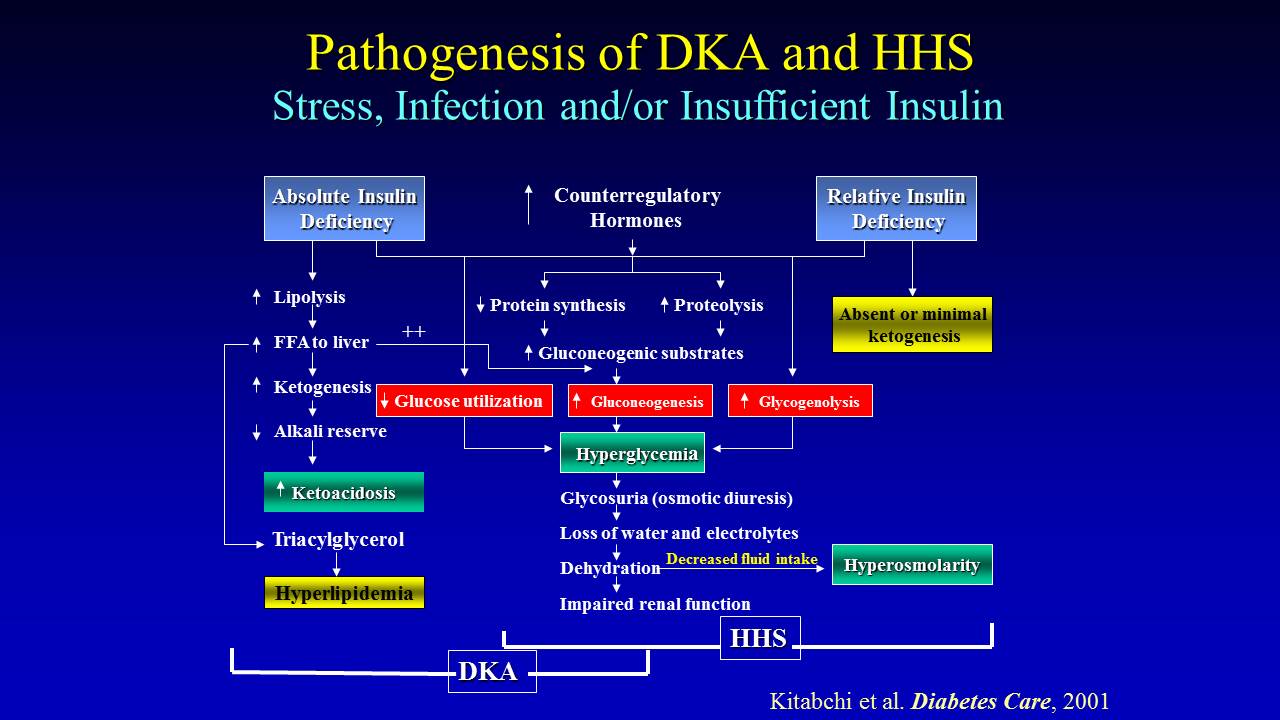 www.clinicaladvisor.comketoacidosis diabetic coma non ketotic dka hhs pathogenesis clinical metabolism
www.clinicaladvisor.comketoacidosis diabetic coma non ketotic dka hhs pathogenesis clinical metabolism
Hyperosmolar States | PaReflectionEd
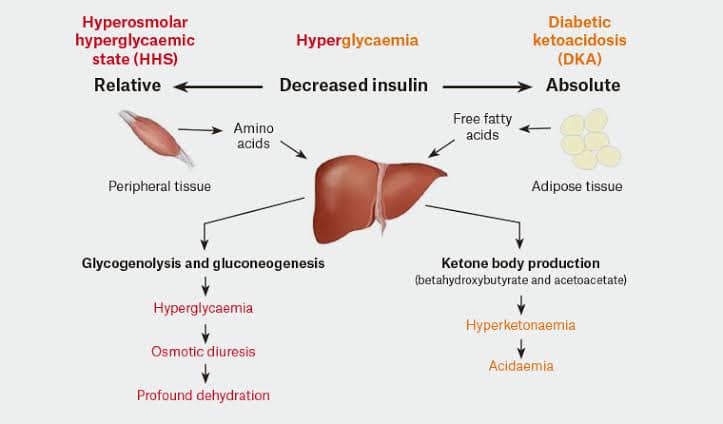 www.paramedicine.educationhyperosmolar ketoacidosis dka diabetic
www.paramedicine.educationhyperosmolar ketoacidosis dka diabetic
Diabetic ketoacidosis and hypersmolar non-ketotic coma. Pin on diabetes. Hyperosmolar ketoacidosis dka diabetic